YWHAE (tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein epsilon)
- symbol:
- YWHAE
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 17p13.3
- gene_family:
- alias symbol:
- FLJ45465
- alias name:
- 14-3-3 epsilon
- entrez id:
- 7531
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000108953
- ucsc gene id:
- uc002fsj.4
- refseq accession:
- NM_006761
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:12851
- approved reserved:
- 1993-09-20
YWHAE(14-3-3ε)属于14-3-3蛋白家族,这是一个高度保守的调控蛋白家族,成员通过结合磷酸化靶蛋白参与细胞信号转导、凋亡、代谢和细胞周期等关键过程。14-3-3蛋白的共性是通过形成同源或异源二聚体,识别含特定磷酸化序列的客户蛋白(如RSXpSXP或RXXXpSXP,其中pS代表磷酸化丝氨酸),从而改变客户蛋白的定位、稳定性或活性。YWHAE作为该家族成员之一,主要定位于细胞质和细胞核,其表达产物14-3-3ε蛋白通过结合多种信号分子(如BAD、CDC25、TP53等)发挥功能。例如,它通过隔离促凋亡蛋白BAD到细胞质来抑制凋亡,或通过稳定CDC25磷酸酶调控细胞周期。YWHAE突变可能导致其与客户蛋白结合能力丧失,进而破坏相关通路。在癌症中,YWHAE基因易位(如与FOXR1融合)会形成致癌融合蛋白,促进肿瘤发生;而在神经发育障碍如Miller-Dieker综合征中,其缺失与大脑皮层发育异常相关。过表达YWHAE可能增强抗凋亡信号导致肿瘤耐药性,或通过过度稳定细胞周期蛋白驱动增殖;而表达降低则可能诱发凋亡增加或细胞周期阻滞。该基因还与神经退行性疾病(如阿尔茨海默病)相关,因其参与tau蛋白病理调控。14-3-3家族其他成员(如YWHAZ、YWHAG)功能部分冗余,但组织分布和客户蛋白偏好存在差异。
This gene product belongs to the 14-3-3 family of proteins which mediate signal transduction by binding to phosphoserine-containing proteins. This highly conserved protein family is found in both plants and mammals, and this protein is 100% identical to the mouse ortholog. It interacts with CDC25 phosphatases, RAF1 and IRS1 proteins, suggesting its role in diverse biochemical activities related to signal transduction, such as cell division and regulation of insulin sensitivity. It has also been implicated in the pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer. Two transcript variants, one protein-coding and the other non-protein-coding, have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2008]
该基因产物属于14-3-3家族,通过结合含有磷酸丝氨酸蛋白介导的信号转导的蛋白质。此高度保守的蛋白家族在植物和哺乳动物中发现,而该蛋白质是100%相同的小鼠直向同源物。它与CDC25磷酸酶,RAF1和IRS1蛋白相互作用,这表明其在与信号转导相关的多种生化活性,例如细胞分裂和对胰岛素的敏感性的调节作用。还已牵涉于小细胞肺癌的发病机制。两个转录物变体,一种蛋白质编码和其它非蛋白质编码,已发现这种基因。 [由RefSeq的,2008年8月提供]
基因本体信息
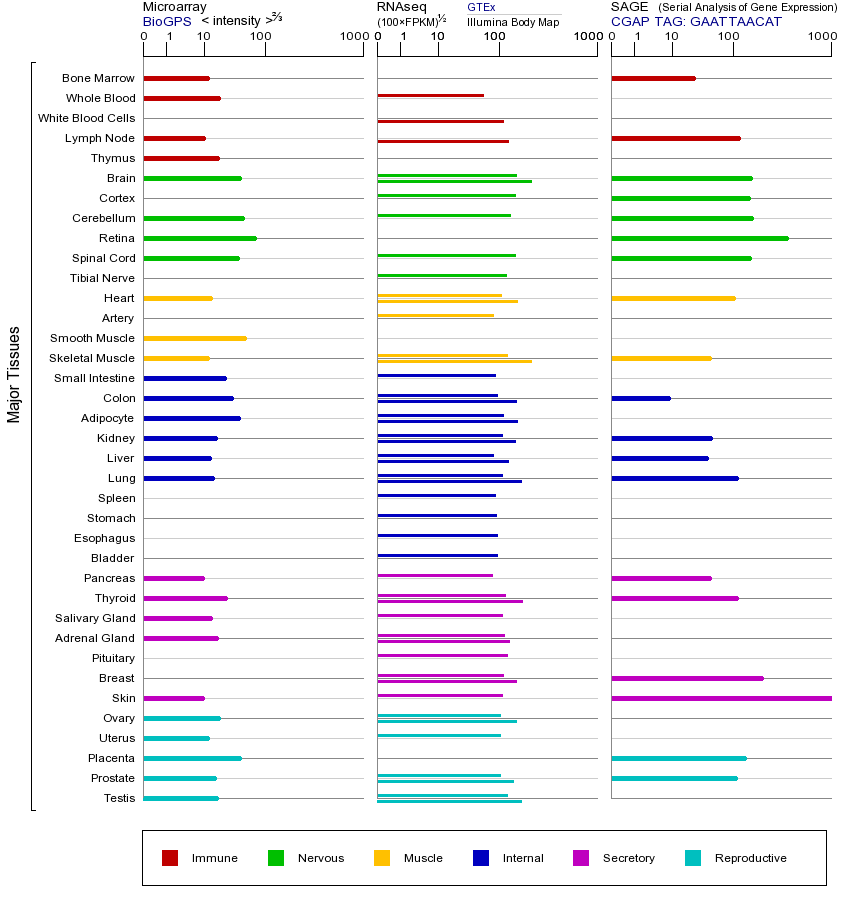
YWHAE基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
YWHAE基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 名称 |
|---|
| 4390 Hippo signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04390] |
| 4151 PI3K-Akt signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04151] |
| 4110 Cell cycle [PATH:hsa04110] |
| 4114 Oocyte meiosis [PATH:hsa04114] |
| 4722 Neurotrophin signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04722] |
| 5203 Viral carcinogenesis [PATH:hsa05203] |
| 5169 Epstein-Barr virus infection [PATH:hsa05169] |
| 名称 |
|---|
| Activation of BAD and translocation to mitochondria |
| Activation of BH3-only proteins |
| Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane |
| Apoptosis |
| Assembly of the primary cilium |
| Cell Cycle |
| Cell Cycle Checkpoints |
| Cell Cycle, Mitotic |
| Cell death signalling via NRAGE, NRIF and NADE |
| Cellular response to heat stress |
| Cellular responses to stress |
| Centrosome maturation |
| Chk1/Chk2(Cds1) mediated inactivation of Cyclin B:Cdk1 complex |
| G2/M Checkpoints |
| G2/M DNA damage checkpoint |
| G2/M Transition |
| Gene Expression |
| Generic Transcription Pathway |
| HSF1 activation |
| Intrinsic Pathway for Apoptosis |
| Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes |
| Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome |
| Membrane Trafficking |
| Mitotic G2-G2/M phases |
| NADE modulates death signalling |
| Organelle biogenesis and maintenance |
| p75 NTR receptor-mediated signalling |
| Programmed Cell Death |
| Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes |
| Regulation of HSF1-mediated heat shock response |
| Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition |
| RHO GTPase Effectors |
| RHO GTPases activate PKNs |
| Signaling by Hippo |
| Signaling by Rho GTPases |
| Signalling by NGF |
| TP53 Regulates Metabolic Genes |
| Transcriptional Regulation by TP53 |
| Translocation of GLUT4 to the plasma membrane |
| Vesicle-mediated transport |
| 疾病名称 | 关系值 | NofPmids | NofSnps | 来源 |
| Miller Dieker syndrome | 0.20434307 | 16 | 0 | BeFree_MGD_ORPHANET |
| Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma | 0.122442977 | 9 | 0 | BeFree_ORPHANET |
| Neoplasm Metastasis | 0.121085767 | 5 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human |
| CHROMOSOME 17p13.3, CENTROMERIC, DUPLICATION SYNDROME | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | ORPHANET |
| Classical Lissencephalies and Subcortical Band Heterotopias | 0.12 | 0 | 0 | CTD_human |
| NONCOMPACTION OF LEFT VENTRICULAR MYOCARDIUM, FAMILIAL ISOLATED, AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT 1 | 0.08 | 0 | 0 | MGD |
| Leukemia, Myelocytic, Acute | 0.039359071 | 145 | 2 | BeFree |
| Preleukemia | 0.010586233 | 39 | 0 | BeFree |
| MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROME | 0.009229024 | 34 | 0 | BeFree |
| Congenital chromosomal disease | 0.008143256 | 30 | 0 | BeFree |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。