RPL28 (ribosomal protein L28)
- symbol:
- RPL28
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 19q13.42
- gene_family:
- L ribosomal proteins
- alias symbol:
- FLJ43307|L28
- alias name:
- 60S ribosomal protein L28
- entrez id:
- 6158
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000108107
- ucsc gene id:
- uc002qkv.4
- refseq accession:
- NM_000991
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:10330
- approved reserved:
- 1997-07-07
RPL28(核糖体蛋白L28)是核糖体的重要组成部分,属于核糖体蛋白(Ribosomal Proteins, RPs)基因家族。核糖体是细胞内负责蛋白质合成的分子机器,由大亚基和小亚基组成,RPL28位于大亚基(60S亚基)中,与其他核糖体蛋白共同维持核糖体结构稳定并参与翻译过程(即mRNA解码为蛋白质的过程)。该基因家族成员通常具有高度保守性(进化中变化极小),在几乎所有物种中广泛存在,主要功能是协助核糖体组装、调控翻译效率及维持细胞稳态。RPL28的表达产物(即RPL28蛋白)除了参与基础翻译外,还可能通过核糖体外的“兼职功能”(moonlighting functions)影响细胞周期、凋亡(程序性细胞死亡)或应激反应(如缺氧或营养缺乏时的细胞应对机制)。 若RPL28发生突变,可能导致核糖体组装缺陷或功能异常,引发核糖体病(ribosomopathies),这类疾病常表现为造血障碍(如贫血)、发育异常或癌症风险增加。例如,某些研究提示RPL28表达异常可能与结直肠癌或白血病进展相关,但具体机制仍需进一步探索。当RPL28过表达时,可能通过提高全局翻译速率促进细胞增殖,但也可能因核糖体失衡触发应激反应;而低表达则可能导致翻译效率下降,影响细胞生长甚至引发凋亡。 此外,RPL28与其他核糖体蛋白存在协同或补偿关系(如RPL5或RPL11),这些蛋白在核糖体应激时可释放并抑制癌蛋白MDM2,从而激活抑癌基因p53。因此,RPL28的表达水平变化可能间接影响p53通路(调控细胞周期和凋亡的关键信号路径)。目前针对RPL28的研究仍在深入,尤其在癌症和遗传性疾病领域,其具体调控网络及治疗潜力有待更多证据支持。
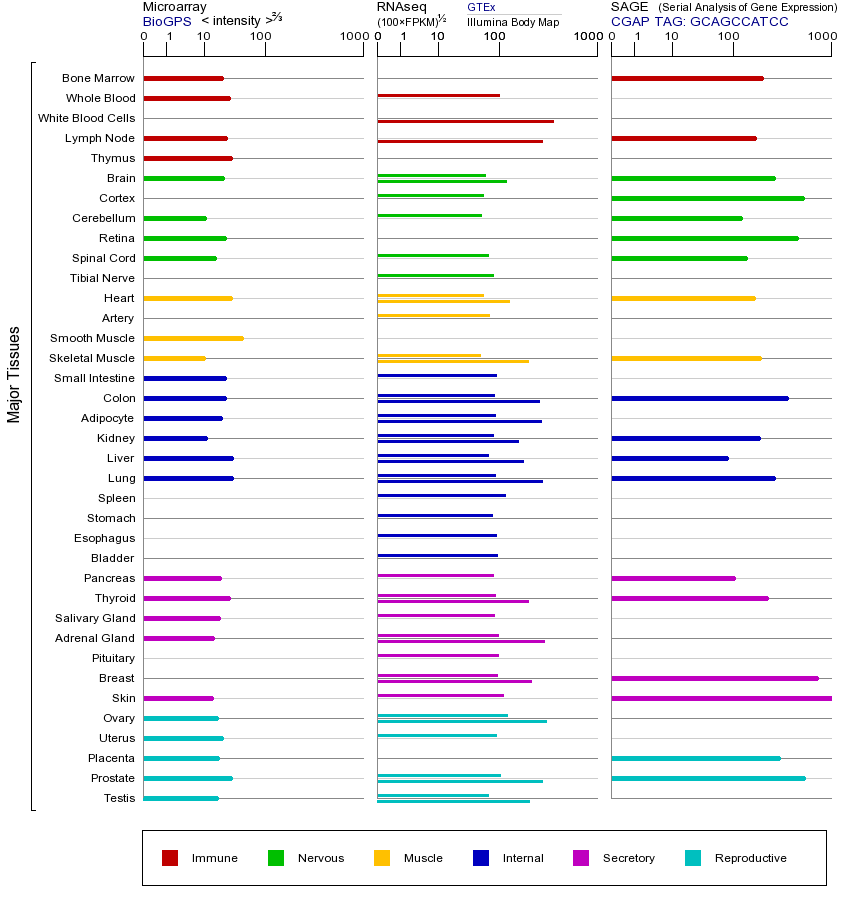
Ribosomes, the organelles that catalyze protein synthesis, consist of a small 40S subunit and a large 60S subunit. Together these subunits are composed of 4 RNA species and approximately 80 structurally distinct proteins. This gene encodes a ribosomal protein that is a component of the 60S subunit. The protein belongs to the L28E family of ribosomal proteins. It is located in the cytoplasm. Variable expression of this gene in colorectal cancers compared to adjacent normal tissues has been observed, although no correlation between the level of expression and the severity of the disease has been found. As is typical for genes encoding ribosomal proteins, there are multiple processed pseudogenes of this gene dispersed through the genome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]
核糖体,催化蛋白质合成的细胞器,由一个小40S亚基和60S大亚基。一起这些亚基组成的4 RNA种类和大约80结构不同的蛋白质。该基因编码一种核糖体蛋白,它是60S亚基的一个组成部分。该蛋白属于L28E家族核糖体的蛋白质。它位于细胞质中。该基因在相比邻近正常组织的结肠直肠癌的可变表达已经观察到,虽然表达水平与疾病的严重程度之间没有相关性已被发现。作为典型编码核糖体蛋白的基因,有该基因通过基因组分散的多个经处理的假基因。在多个转录剪接变异体导致不同的编码亚型。[由RefSeq的,2008年10月提供]
基因本体信息
RPL28基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
RPL28基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 名称 |
|---|
| 3010 Ribosome [PATH:hsa03010] |
| 名称 |
|---|
| 3' -UTR-mediated translational regulation |
| Cap-dependent Translation Initiation |
| Disease |
| Eukaryotic Translation Elongation |
| Eukaryotic Translation Initiation |
| Eukaryotic Translation Termination |
| Formation of a pool of free 40S subunits |
| Gene Expression |
| GTP hydrolysis and joining of the 60S ribosomal subunit |
| Infectious disease |
| Influenza Infection |
| Influenza Life Cycle |
| Influenza Viral RNA Transcription and Replication |
| L13a-mediated translational silencing of Ceruloplasmin expression |
| Metabolism of proteins |
| Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) |
| Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) |
| Nonsense-Mediated Decay (NMD) |
| Peptide chain elongation |
| SRP-dependent cotranslational protein targeting to membrane |
| Translation |
| Viral mRNA Translation |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。