PLAU (plasminogen activator, urokinase)
- symbol:
- PLAU
- locus group:
- protein-coding gene
- location:
- 10q22.2
- gene_family:
- alias symbol:
- URK|UPA
- alias name:
- None
- entrez id:
- 5328
- ensembl gene id:
- ENSG00000122861
- ucsc gene id:
- uc001jwa.4
- refseq accession:
- NM_002658
- hgnc_id:
- HGNC:9052
- approved reserved:
- 2001-06-22
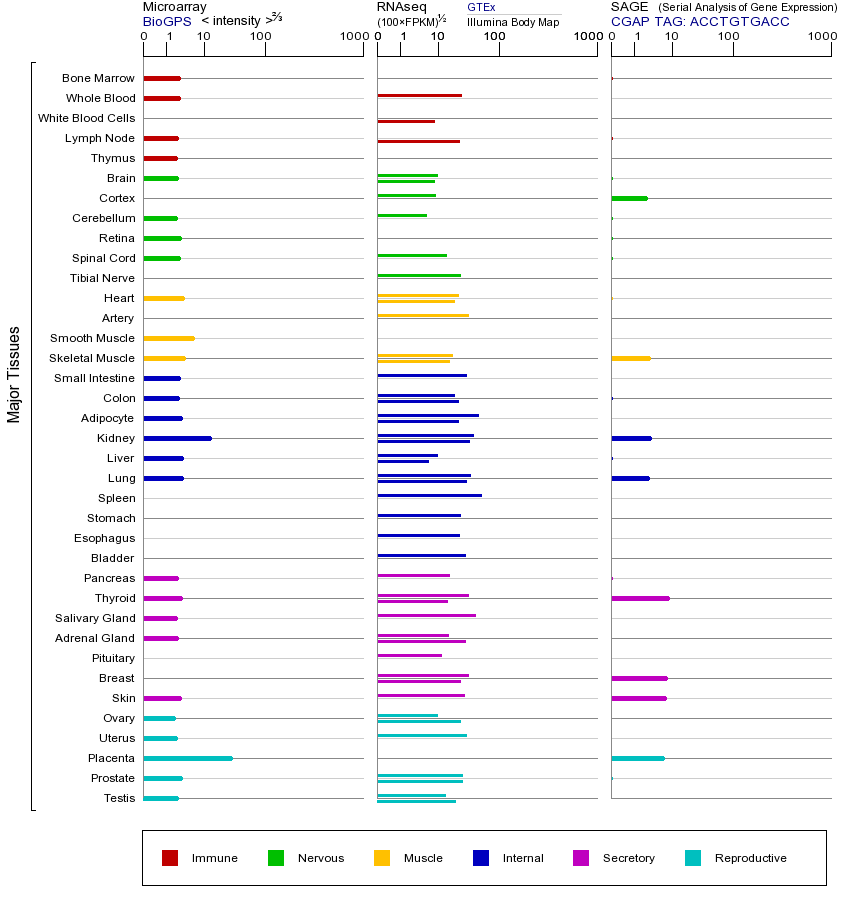
PLAU基因编码尿激酶型纤溶酶原激活剂(uPA),这是一种丝氨酸蛋白酶,在纤溶系统中发挥关键作用。uPA的主要功能是将纤溶酶原转化为纤溶酶,从而降解纤维蛋白和其他细胞外基质成分,参与组织重塑、伤口愈合、炎症反应和肿瘤转移等过程。uPA通过与细胞表面的uPAR受体结合发挥作用,其活性位点位于蛋白酶结构域。PLAU基因突变可能导致纤溶系统功能异常,与血栓形成、出血性疾病或肿瘤侵袭性增加相关。研究表明,PLAU过表达与多种癌症的进展和转移密切相关,如乳腺癌、结肠癌和肺癌,因其促进肿瘤细胞侵袭和血管生成;而PLAU表达降低可能减少肿瘤转移风险,但可能影响正常组织修复。PLAU属于纤溶酶原激活剂基因家族,该家族还包括组织型纤溶酶原激活剂(PLAT),两者均通过激活纤溶酶原参与纤溶过程,但uPA更侧重于细胞迁移和组织重塑,而tPA主要参与血管内血栓溶解。PLAU还参与细胞信号传导,影响细胞增殖、黏附和迁移。此外,PLAU与阿尔茨海默病等神经退行性疾病有关,因其可能影响β-淀粉样蛋白的清除。在炎症中,PLAU通过调节免疫细胞迁移参与炎症反应。该基因的表达受多种因素调控,包括生长因子、细胞因子和激素等。
This gene encodes a serine protease involved in degradation of the extracellular matrix and possibly tumor cell migration and proliferation. A specific polymorphism in this gene may be associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease and also with decreased affinity for fibrin-binding. This protein converts plasminogen to plasmin by specific cleavage of an Arg-Val bond in plasminogen. Plasmin in turn cleaves this protein at a Lys-Ile bond to form a two-chain derivative in which a single disulfide bond connects the amino-terminal A-chain to the catalytically active, carboxy-terminal B-chain. This two-chain derivative is also called HMW-uPA (high molecular weight uPA). HMW-uPA can be further processed into LMW-uPA (low molecular weight uPA) by cleavage of chain A into a short chain A (A1) and an amino-terminal fragment. LMW-uPA is proteolytically active but does not bind to the uPA receptor. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Feb 2009]
该基因编码参与细胞外基质的降解,并可能肿瘤细胞迁移和增殖的丝氨酸蛋白酶。在该基因的具体多态性可能与迟发型阿尔茨海默氏病相关联,并且还具有降低的亲和力的纤维蛋白结合。这种蛋白由纤维蛋白溶酶原的精氨酸 - 瓦尔债券的具体裂解转化纤溶酶原为纤溶酶。纤溶酶反过来切割该蛋白在一个赖氨酸 - 异亮氨酸键,以形成在其中单个二硫键的氨基末端A链连接到催化活性,羧基端B链的两链衍生物。该双链衍生物也称为HMW-uPA的(高分子量的uPA)。 HMW-uPA的可以由链A的切割进一步加工成LMW-uPA的(低分子量的uPA)成短链中的(A1)和氨基末端片段。 LMW-uPA的是蛋白水解活性的,但不绑定到特异受体。已发现该基因编码不同亚型选择性剪接转录变异体。 [由RefSeq的,2009年2月提供]
基因本体信息
PLAU基因(以及对应的蛋白质)的细胞分布位置:
- 质膜
- 细胞质
- 细胞外
- 高尔基体
- 囊泡
- 细胞骨架
- 内质网
- 细胞核
- 内体
- 溶酶体
- 线粒体
PLAU基因的本体(GO)信息:
| 名称 |
|---|
| 4064 NF-kappa B signaling pathway [PATH:hsa04064] |
| 4610 Complement and coagulation cascades [PATH:hsa04610] |
| 5202 Transcriptional misregulation in cancers [PATH:hsa05202] |
| 5206 MicroRNAs in cancer [PATH:hsa05206] |
| 5205 Proteoglycans in cancer [PATH:hsa05205] |
| 名称 |
|---|
| Dissolution of Fibrin Clot |
| Hemostasis |
| 疾病名称 | 关系值 | NofPmids | NofSnps | 来源 |
| Alzheimer's Disease | 0.225099593 | 6 | 0 | CTD_human_GAD_LHGDN_MGD |
| Myocardial Infarction | 0.202638474 | 8 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human_GAD_RGD |
| Intracranial Hemorrhages | 0.2 | 5 | 0 | CTD_human_RGD |
| Asthenozoospermia | 0.2 | 1 | 0 | CTD_human_RGD |
| Thrombosis | 0.2 | 7 | 0 | CTD_human_RGD |
| Brain Edema | 0.2 | 2 | 0 | CTD_human_RGD |
| Reperfusion Injury | 0.2 | 2 | 0 | CTD_human_RGD |
| Neoplasm Metastasis | 0.150964236 | 97 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human_LHGDN |
| Prostatic Neoplasms | 0.136346101 | 8 | 0 | CTD_human_LHGDN |
| Asthma | 0.128715934 | 5 | 0 | BeFree_CTD_human_LHGDN |
联系方式
山东省济南市章丘区文博路2号 齐鲁师范学院 genelibs生信实验室
山东省济南市高新区舜华路750号大学科技园北区F座4单元2楼
电话: 0531-88819269
E-mail: product@genelibs.com
微信公众号
关注微信订阅号,实时查看信息,关注医学生物学动态。